Introduction
- An operation code(opcode) of an instruction specifies the operation to be performed on data. This operation is mainly executed on some data stored in a register or memory. Operands may be specified in one of the three basic forms i.e., immediate, register, and memory.
- Conventions:
- In this addressing scheme, the symbols A, A1, A2 … etc. denote the content of an operand field i.e. Ai may refer to a data or a memory address.
- In case, the operand field is a register address, then the symbols R, R1, R2,… etc., are used.
- If C denotes the contents (either of an operand field or a register or of a memory location), then (C) denotes the content of the memory location whose address is C.
- The symbol EA (Effective Address) refers to a physical address in a non-virtual memory environment and refers to a register in a virtual memory address environment.
- The symbols D, D1, D2,…, etc. refer to actual operands to be used by instructions for their execution.
- The symbols X, Y, etc. denotes memory variables.
Definition
- The different ways/formats in which the location of an operand is specified in an instruction are called Addressing mode.
- In other words, addressing schemes/modes is the mechanism applied for specifying operands i.e. how operands are interpreted.
Features
- Different computer architectures vary greatly as to the number of addressing modes they provide in hardware. Generally, most RISC architectures have about five simple addressing modes, while CISC architectures may have over a dozen addressing modes.
Types
- There are multiple ways of addressing schemes due to multiple instruction formats. Selecting an appropriate scheme will impact not only the ease of writing the compiler but will also determine how efficient the architecture can be.
- All computers employ more than one addressing scheme to give programming flexibility to the user by providing facilities such as pointers to memory, loop control, indexing of data, program relocation, and reducing the number of bits in the operand field of the instruction.
- The tree representations of common addressing schemes/modes are –
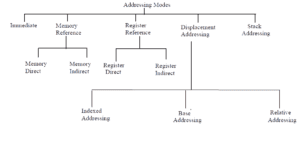
(A) Immediate Addressing Mode :
- In this mode, the operand is the data in the operand address field of the instruction. Since there is no address field at all, and hence no additional memory accesses are required to execute this instruction. Here, Data is present in the instructions and Load the immediate data to the destination provided directly.
- Here, the operand is specified in the instruction itself.
- In this addressing scheme, the actual operand D is A because the operand is actually present in the instruction as a part and hence the content of the operand field: i.e. D = A.
- The effective address in this case is not defined.
- A # sign is used conventionally in front of the value to indicate that the value is Immediate.
- When an operand is interpreted as an immediate value, then the actual value say 5 is put in the CPU register directly.
- Example:
- MOV X, 5
- MOV AL, 23h
- MOV BX, 0235h
- MOV [1011h], 245h
- ADD AX, 652h
Advantages:
-
- This addressing mode is used to initialize or set the value of a variable and define and use constant value.
- No additional memory accesses/references are required during the execution of the instruction.
- It is a fast addressing mode.
Disadvantages:
-
- In this mode, the size(magnitude) of the instruction and operand field is limited. Therefore, the type of data specified under this addressing scheme is also restricted. For example, if an instruction of 16 bits uses 6 bits for opcode and 2 bits for addressing mode, then 10 bits can be used to specify an operand. Thus, 210 possible values only can be assigned.
(B) Memory Reference :
(i) Memory Direct (Direct Addressing):
-
- The address of the data is given explicitly/directly in the instruction.
- This addressing mode is used to accept data from outside devices to store in the accumulator or send the data stored in the accumulator to the outside device.
- In this mode, the data is accepted from port 00H and stored in the accumulator or Send the data from the accumulator to the port 01H.
- This addressing mode is widely used to provide global variables and less often for local variables during processing.
- Example:
- Example:
MOV AX, [1234h](Move the contents of memory location 1234h into register AX)
- Example:
(ii) Memory Indirect (Indirect Addressing):
-
- The address of the data is given indirectly through a register. This means that the Effective Address is calculated by the processor. The contents of the address (and the one following) are used to form a second address. The second address is where the data is stored.
- Example:
MOV AX, [BX](Move the contents of the memory location pointed to by BX into register AX)- MOV X, [*Y]
(C) Register Reference :
(i) Register/Register Direct :
-
- This addressing mode is frequently used for storing data as local variables of procedures.
- In this mode, Data is provided through the registers.
- In this, the operand is placed in one of the 16-bit or 8-bit general purpose/data registers.
- Example:
- MOV DX, AX
- MOV AX, CX
- ADD AL, BL
- ADD CX, DX
(ii) Register Indirect :
-
- This mode uses a register to hold the address of the data.
- In this addressing scheme, the operand is data located in the memory pointed to by a register.
- This is almost the same as the indirect addressing scheme except it is much faster than indirect addressing that requires two memory accesses.
-
The effective address of the operand in this scheme is calculated as:
-
-
The address capability of the register’s indirect addressing scheme is determined by the size of the register.
- Example:
MOV AX, [BP](Move the contents of the memory location pointed to by BP into register AX)- MOV AX, BX
-
(D) Displacement Addressing Mode :
(i) Indexed Addressing Mode :
-
- This addressing mode is used to access specific data members from an array.
- It combines a base address with an index offset.
- Example:
MOV AX, [BX+SI](Move the contents of the memory location at address (BX+SI) into register AX)- MOV DI, SI
(ii) Base Addressing Mode :
-
- This addressing mode is employed to relocate the programs in memory, especially in multi-programming systems.
- Example :
- MOV AX, [BX+0]
(iii) Base-Indexing Addressing Mode :
-
- This mode is the hybrid form of Base and Indexed Register.
- This mode uses a base register and an index register with an optional offset.
- Example:
MOV AX, [BX+SI+10h](Move the contents of the memory location at address (BX+SI+10h) into register AX)
(iv) Relative Addressing Mode :
-
- This address is relative to the current value of the program counter (PC).
- In this addressing scheme, the register R stores the program counter (PC) value that contains the address of the current instruction being executed. The operand field A contains the displacement (positive or negative) of an instruction or data with respect to the current instruction.
- This addressing scheme has advantages if the memory references are nearer to the current instruction being executed.
- Example:
- Example: JMP label_name (Jump to the address relative to the current instruction pointer)
- MOV AX, (BX+5)
(E) Stack Addressing Mode :
- In this addressing scheme, the operand is implied as the top of the stack. It is not explicit, but implicit.
- It uses a CPU register, called Stack Pointer (SP). The SP points to the top of the stack i.e. to the memory location where the last value was pushed.
- A stack addressing provides a sort of indirect addressing and indexed addressing.
- This is not a very common addressing scheme. Here, the operand is found on the top of a stack. In some machines, the top two elements of the stack and the top of the stack pointer are kept in the CPU registers, while the rest of the elements may reside in the memory.
- This addressing mode is used to provide local variables during processing.
- Example:
- ADD POP (pop the top two items from stock and add them)
- EA=Top of Stock
Use/Applications
- In general, not all addressing modes are used for all applications. However, some of the common areas where compilers of high-level languages use them.
-
Addressing Mode Uses/Applications Immediate Mode For moving constants(values) in memory and initialization of variables Memory Direct Used for global variables and less often for local variables Register Direct Used for storing local variables of procedures Register Indirect For holding pointers(address) to structure in programming languages C Indexed Addressing To access local data members/variables of an array in an iterative way Base (Register) Addressing Used to relocate the programs in memory especially in multi-programming systems Stack Addressing Used for local variables supplying Auto-index mode For pushing or popping the parameters of procedures
![]()
0 Comments