Output Units
- Output Units or devices display the result of input data or signals after processing it.
- Output is the process of producing results from the data for getting useful information.
- Output devices display information on the screen (monitor) or the printer and send information to other computers.
- Output devices also display messages about what errors may have occurred and bring up a message or dialog box asking for more information to be input.
- The output is also stored inside the computer for further processing.
- An output device is used to send data out of the system.
Examples of Output Units
- Examples of major output units or devices are: –
- Monitor
- Printer
- Plotter
- Speaker
Monitor
-
Monitors display what is going on in the computer.
-
They can run at various resolutions. It is the part of a computer that looks like a TV set.
Classification of Monitors
(a) Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) Monitor
-
-
-
The main components of CRT monitors are the electron gun, the electron beam controlled by an electromagnetic field, and the phosphor-coated display screen.
-
These older monitors are bulky and require a lot of space for installation.
-
CRT Monitors display what is going on in your computer.
-
They can run at various resolutions. It is part of a computer that looks like a TV set.
- In CRT monitors, the image is projected on the screen by directing the electron beam onto the computer screen. To precisely direct the electron beams, copper steering coils are used to create a magnetic field inside the tube. By applying varying voltages to the copper coils a beam can be positioned at any point on the screen.
-
-
(b) Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD) Monitor
-
-
- First introduced in watches and clocks in the1970’s,
- LCDs are now used to display images on monitors.
- A newer technology in computer screens is TFT LCD monitors. These are lightweight monitors and are used in laptop computers.
- Active matrix structure is used by most modern LCD monitors and television sets.
- In this technology, a matrix of thin-film transistors (TFT) is added to the polarizing and color filters.
- It enhances the display to make it look brighter and sharper. It can also produce much better images and have quicker response times.
- These monitors are portable, reliable, and consume less electricity.
- Images produced by these monitors are of better quality than that of old CRT monitors.
- The LCD monitors have very high resolution and emit less radiation than CRT monitors.
- The screen is also flickering-free.
-
(c)Thin Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display (TFT LCD) Monitor
-
-
- It is a type of monitor that uses thin film transistor technology to enhance the image quality of LCD Monitors.
- These are used as monitors in television sets, desktop computers, laptop computers mobile phones, etc.
-
(d) Light Emitting Diodes (LED) Monitors
-
-
- Light Light-emitting diodes (LED) are the latest technology that is being used nowadays for making high-definition TV screens and monitors.
- It is a semi-conductor light source.
- In this technology, diodes are used to light up the screen instead of liquid crystal Diodes.
- LED is known as a light-emitting diode.
- It is an electronic device that lights up when electricity is passed through it.
- LEDs are usually red.
- They are good for displaying images because they can be relatively small, and they do not burn out.
- However, they require more power than LCD monitors.
- LED is a lightweight monitor and is used in laptop computers and on TV.
- The Life of LED monitors is three times that of LCD monitors and they have less warm-up time than that of CRT or LCD monitors.
- These monitors require less space on the desk, less power consumption, and have a flicker-free screen.
-
(e) Projection Displays
-
-
- These are normally used for large group presentations.
- These systems can be connected to a computer and whatever appears on the computer terminal gets enlarged and projected on a large screen.
- Video projector receives video signals and projects the corresponding image on a projection screen.
- It uses a lens system for this projection.
- These are popularly used for seminars, classroom lectures, marketing presentations conference room presentations, etc.
-
[B] Based on color capabilities, monitors can be divided into –
(a) Monochrome Monitor
-
-
- These monitors display the result in two colors, i.e., black/white, green/black, and amber/black.
- One color is for the background of the screen and the other is for the foreground.
-
(b) Gray Scale Monitor
-
-
- It is a monochrome type of monitor. But it displays the output by using different shades of gray, made by a combination of black and white.
-
(c) Color Monitor
-
-
- It can display the output in many colors, ranging from 16 to over 1 million different colors.
- These are also called RGB monitors because they accept three separate signals, which are red, green, and blue.
-
[C] Based on monitor size/screen size, they are of the following types –
(The size of the computer screen is measured in diagonal inches and is given by measuring the distance from one corner to the opposite corner (diagonally).)
(i)14 inches Monitor
-
-
- The smallest size for VGA monitors is 14 inches, which is also the entry-level monitor for most computer systems.
- It is now not used practically.
-
(ii) Landscape Monitor
-
-
- The Larger-size landscape monitors can display two full pages side by side at a time.
- Landscape Monitor sizes are 17 inches, 20 inches, 23 inches, etc.
-
[D] Based on monitor screen resolution, they are of the following types –
(a) SD Monitor
-
-
- Most modern monitors that use resolutions below 1080 pixels are called SD monitors.
-
(b) HD Monitor
-
-
- Some high-end models of computer monitors use display 1280 by 1024, or even 1600 by 1200 pixels and are called HD monitors.
-
(c) Full High Definition Monitor
-
-
- It has at least/greater display resolution of 1920 x 1080 pixels. Resolution explains how many pixels a display has in length x width format.
- FHD displays are also referred to as 1080p.
-
[E] Based on the type of signal they accept to display the contents they are divided into –
(a) Analog Monitor
-
-
- When a monitor works using the electronic signal that is sent by signals of varying frequency, amplitude, or phase instead of being sent as an ON or OFF data transmission is called an analog signal. Analog signals allow equipment to handle information that continuously changes such as voltage, current, etc.
- Analog signals can be represented by a wave sign and watches which change their position continuously.
- These are the traditional type of color monitors and are based on CRT technology. These work like the television screen and accept analog signals.
-
(b) Digital Monitor
-
-
- An electronic signal that is sent as binary digits of either ON or OFF is called a Digital signal.
- In this, signals are either 0 or 1 i.e. up or down for ON and OFF mode.
- Here a pixel is either ON or OFF helping to create an image on the display screen.
- The digital monitor receives digital signals and can use CRT technology.
- The data in these monitors is received from the video adapter.
- These are of different types such as CGA (Color Graphics Adapter), EGA (Enhanced Graphics Adapter), VGA (Video Graphics Array), and SVGA (Super Video Graphics Array).
- These are fast and produce clear images.
-
Printers
- It is one of the most important output devices.
- Printers are used for producing output on paper i.e. to produce a hard copy of the output.
- Print speed, quality, printer resolution, reliability, and the costs of toner are the major deciding factors for choosing a printer.
Classification of Printers
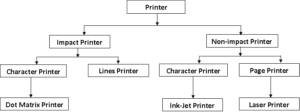
[A] Based on printing mechanism/technology, printers are classified into: –
(A) Impact Printers (B) Non-impact Printers
(A) Impact Printers –
-
- Impact printers use variations of the standard typewriter printing mechanism where a hammer strikes the paper through an inked ribbon.
- Character and Line Printers are in this category.
- Examples are – Daisy, Drum, and Dot Matrix Printer.
(B) Non-Impact Printers –
-
- A non-impact printer uses chemical, heat, or electrical signals to produce symbols on paper.
- Some of these require special coated or treated paper to print characters on them.
- Examples are – Ink-jet and Laser Printer.
[B] Based on printing methods, printers are classified into: –
(A) Character Printer –
-
- These printers can print only one character at a time.
- They work similar to a typewriter.
- Character printers are also called “Light duty” Printers.
- Examples are – Daisy Wheel Printer, Dot Matrix Printer, and Inkjet Printer.
(B) Line Printer –
-
- Line printer prints a line at a time.
- Line printers are also called “heavy-duty” printers.
- They are high-speed printers.
- Line printers are still widely used in data centers and industrial environments and can print multi-part forms at a very rapid rate.
- The two main types of line printers are chain printers and drum printers.
- Examples are – Dot Matrix, Drum, Band, Bar, Comb, Wheel and Chain Printer.
(C) Page Printer –
-
- A page printer is a printer that processes and prints a whole page at a time.
- Laser printers and also inkjet printers are considered page printers.
- A page printer is a hardware device that prints one full page at a time, ejects that page, and then feeds in the next page to be printed.
[C] Based on printing speed in terms of time, printers are classified into: –
(A) Low Speed Printer –
-
- Character Printers are in this category.
- They may be either impact or non-impact types of printers.
- Examples are – Dot matrix, Daisy wheel, Golf ball, Thermal, Inkjet, etc.
(B) High-Speed Printer –
-
- Lines and Page Printers are in this category.
- They may be either impact or non-impact types of printers.
- Examples are – Drums, Chains, Electrostatic, Laser Printers, etc.
Chain Printer –
- It is the character printer.
- An obsolete type of solid-font line printer in which the font was etched or engraved on small plates linked together to form a chain.
- An early line printer that used type slugs linked together in a chain as its printing mechanism.
- The chain spins horizontally around a set of hammers.
- The print element in a chain printer is a metallic band or chain containing the embossed characters that rotates horizontally in front of the paper.
- A complete chain consists of five sections; each section consists of 48 characters.
- As the print chain rotates, properly timed print hammers strike the paper along with the linked ribbon, against the proper character on the chain as it passes.
- Chain printers are one of the fastest impact printers that can produce up to 400 to 2500 characters per second.
- Chain Printers also called Band Printers, contain characters on a rotation band.
- Speeds of up to 3000 lines a minute may be possible with these machines.
Drum Printer –
- A wide-form of inkjet printer.
- The paper is taped onto a drum for precise alignment to the nozzles.
- An old line printer technology that formed character images around a cylindrical drum as its printing mechanism. When the desired character for the selected position rotated around to the hammer line, the hammer hit the paper from behind and pushed it into the ribbon and onto the character.
- The hammer pushes the paper into the type slug when it rotates around to the proper position. Such printer technologies seem ridiculous compared to the quiet, high-speed workings of today’s laser printers.
Serial Printer –
- A printer that prints one character at a time in the sequence in which they appear in the line of text.
- The sequence may be taken from left to right.
- A printer that attaches to a computer through a serial interface. Because of slow printing speed and compatibility issues, the serial printer has more or less been replaced by the USB printer.
- All serial printers have an arrangement in which a print head moves parallel to the paper and along the line to be printed.
- The term serial printer refers to the method of printing and not to the connection, which may be serial or parallel.
- Early serial printers used a computer interface called “RS-232.”
Thermal Printer –
- A thermal printer comprises of : –
-
- Thermal head: generates heat and then prints on paper
- Platen: a rubber roller that feeds paper
- Spring: applies pressure to the thermal head, causing it to contact the thermo-sensitive paper
-
- Thermal Printing is a digital printing process that produces a printed image by selectively heating coated thermal paper when the paper passes over the thermal print head.
- The coating turns black in the areas where it is heated, producing an image.
- Two-color direct thermal printers can print both black and an additional color (often red) by applying heat at two different temperatures.
- Thermal printers print more quietly and usually faster than impact dot matrix printers.
- They are also smaller, lighter, and consume less power, making them ideal for portable and retail applications.
- Thermal printers have no ink, toner, or ribbon.
Daisy-Wheel Printer –
-
- This printer is similar to a ball-head typewriter.
- This type of printer has a plastic or metal wheel on which the shape of each character is embossed.
- A hammer presses the wheel against a ribbon, which in turn makes an ink stain in the shape of the character on the paper.
- Daisy-wheel printers produce letter-quality print but cannot print graphics.
- The print quality of this impact printer is very low as is the speed.
- These are practically obsolete now.
Dot Matrix Printer
- This is one of the most popular printers used for personal computing systems.
- These printers are relatively cheaper compared to other technologies and use impact technology.
- Characters in this printer are formed by the combination of dots.
- A Dot-Matrix printer creates characters by striking pins against an ink-soaked ribbon.
- Each pin makes a dot and combinations of dots form characters and illustrations. The moving portion of the printer is called the print head.
- In the 1970s and 1980s, dot matrix impact printers were generally considered the best tradeoff between expense and versatility, and until the 1990s they were by far the most common form of printers used with personal computers.
Advantages
-
- Dot matrix printers, like any impact printer, can print on multi-part stationery or make carbon copies.
- These Impact printers have one of the lowest printing costs per page. As the ink is running out, the printout gradually fades rather than suddenly stopping part of the way through a job.
- They can use continuous paper rather than requiring individual sheets, making them useful for data logging.
- They are good, reliable, and ideal for use in situations where printed content is more important than print quality.
Disadvantages
-
- Impact printers are usually noisy.
- They can only print low-resolution graphics, with limited color performance, and limited quality.
- These printers are slow. Speed can be 225 cps to 250 cps. Speed may vary from one printer to another.
Line Printer
- As the name suggests, a line printer is a high-speed printer that is used to print one entire line of text at a time.
- Line printers are used to print large amounts of data, printing labels, accounting work, and other large business printing applications in data centers.
- These are fast printers ranging in speed from 300 to 2500 lines per minute.
- Examples are Drum Printers and Chain Printers.
Page Printer
- These are very high-speed printers that produce high-quality output.
- Their speed ranges from 10-25 pages per minute.
- These printers are commonly used today.
- They use modern Laser Printer technology and print a whole page in one go.
- There are many varieties of laser page printers and so their prices range from base level upwards.
Ink-jet Printer
- The Inkjet printer works on inkjet technology and produces better quality printouts than dot matrix printers.
- They print by spraying a controlled stream of tiny ink droplets accurately on the paper forming either dot matrix or solid characters.
- The printing quality of these printers is very good with a speed of 700 or more characters per second.
- These are non-impact and hence are relatively silent during the printing process.
- These printers are easy to use and can be used to print color pages.
Advantages
Compared to other printers, inkjet printers have several advantages. These are –
-
- They are quieter in operation than impact printers.
- They can print finer, smoother details through higher print head resolution.
- They can produce photographic-quality text and images.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of Inkjet printers are: –
-
- The ink is often very expensive.
- Many intelligent ink cartridges contain a microchip that communicates the estimated ink level to the printer; this may cause the printer to display an error message, or incorrectly inform the user that the ink cartridge is empty.
- The very narrow inkjet nozzles are prone to clogging with dried ink.
Laser Printer
- This is a high-quality, high-speed, and high-volume technology printer.
- In laser printers, a laser beam is used to produce an image on a drum. The light of the laser alters the electrical charge on the drum wherever it hits it. The drum is then rolled through a reservoir of toner, which is picked up by the charged portions of the drum. Finally, the toner is transferred to the paper through a combination of heat and pressure.
- Laser printers produce very high-quality text and graphics but are expensive.
- The technology used by them is the same as that of photocopying machines.
- The speed of laser printers varies from 10 pages per minute to 200 pages per minute.
- Laser printers are also called page printers; because they print a whole page in one go.
- Standard laser printers can be classified into two categories in terms of color: –
(a) Monochrome Laser Printer
-
- Monochrome laser printers use a single toner.
(b) Color Laser Printer
-
- Color laser printers use four toners to print in full color.
- These printers are about five to ten times as expensive as their monochrome siblings.
- Color laser printers are popular and are being widely used, despite their cost.
- To print documents with graphics and photographs a color laser printer is a good option.
Plotters
- A Plotter is a device that draws pictures on a page as output, after receiving a print command from the computer.
- It is also called a graph plotter.
- In plotters, pens are used to draw lines on the paper, which is placed in the plotter.
- Plotters produce high-quality diagrams on paper and their output quality is good.
- Engineers, architects, and planners use plotters to generate high-quality, high-precision graphic output of different sizes.
- For several design applications such as the design of the layout of an aircraft, car, and architectural design of a building, and in other computer-aided design applications plotters are very useful.
- A plotter is of two types:
- Drum Plotter
- Flat-Bed Plotter
- The drum plotters are generally smaller than flatbed plotters and they have lower resolutions than flatbed plotters.
- HP, Canon, and Epson are the popular companies that manufacture good quality platters.
Speakers
- Speakers and Microphones Speakers, Computer speakers, or multimedia speakers, are external speakers, commonly equipped with a low-power internal amplifier that produces sound as output.
- External speakers are connected to a computer by using a plug and socket.
- Computer speakers range widely in quality and price.
- Laptop computers have built-in speakers.
![]()
0 Comments