Definition of Procedure
- In VB.NET, a Procedure is a block of reusable code that performs a specific task.
Exit Statements in Procedure
- The term Exit Sub or Exit Function is used to terminate the execution of program prematurely/forcibly.
Types of Procedure
Procedures can be of two types:
- Subroutine Procedures:
- Function Procedures:
Subroutine Procedures
- In VB.NET, a Subroutine is a block of reusable code that performs a specific task or action but does not return a value.
- A Sub procedure executes a block of code without returning any value.
- Syntax :
- Example :
- Types of Subroutine
- To call/use a subroutine in a program, simply use the subroutine procedure name in the program where it is required. [Here, DisplayMessage() is in the above example.]
- There are two types of Subroutine – (i) Subroutine without Parameters (ii) Subroutine with Parameters
- Subroutine without Parameters (Non-Parameterized Subroutines) :
-
- Subroutine with Parameters (Parameterized Subroutines):
Function Procedures
- In VB.NET, a Function is a block of reusable code that performs a specific task or action but returns a value.
- Syntax :
- Example :
- Types of Function :
- To call/use a Function in a program, simply use the Function procedure name in the program where it is required. [Here, AddNumbers() is in the below example.]
- There are the following types of Functions in VB .Net, depending on their purpose, behavior, and usage –
- In-Built Functions/Built-in Functions/Library Functions/Pre-defined Functions
- User-defined Functions/Standard Functions
- Recursive Functions
- Overloaded Functions
- Shared Functions
(A) Built-in Functions
There are the following categories of in-built functions or library functions available in VB .net : –
(1.) VB Math in-Built Functions
- CInt()
- This function is used to convert the value(practically numeric) of different data types into an integer type.
- Syntax: CInt(val)
- Fix()
- Fix Function in Visual Basic.net is used to return the integer part of the given number. But when the number is negative it returns a negative number greater than or equal to the number.
- Syntax: Fix(Number)
- Example:
Sub Main()
Console.WriteLine(“Integer part of 12.27 is: ” & Fix(12.27))
Console.WriteLine(“Integer part of 0.23 is: ” & Fix(0.23))
Console.WriteLine(“Integer part of -4.2 is: ” & Fix(-4.2))
Console.WriteLine(“Integer part of -8.8 is: ” & Fix(-8.8))
End Sub
End Module
Integer part of 0.23 is: 0
Integer part of -4.2 is: -4
Integer part of -8.8 is: -8
- Hex()
- The Hex() function is used to convert the corresponding number into its Hexadecimal value.
- Syntax: Hex(number)
- Math.Abs():
- Math.Abs() Function in VB.net is used to return the absolute value of a number.
- Syntax: Math.Abs(number)
- Example:
Sub Main()
Console.WriteLine(“Absolute Value of -5 is = ” & Math.Abs(-55))
Console.WriteLine(“Absolute Value of 5.5 is = ” & Math.Abs(-5.53))
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
Absolute Value of 5.5 is = 5.53
- Math.Exp():
- The Math.Exp() function returns the exponential value of a number.
- Syntax: Math.Exp(num)
- Math.Log():
- The Math.Log() function returns the natural logarithm of a number.
- Syntax: Math.Log(num)
- Math.Sqrt()
- The Math.Sqrt() function is used to return the square root of a number(num).
- Syntax: Math.Sqrt(num)
- Oct()
- The Oct() function is used to convert the corresponding number into its Octal value.
- Syntax: Oct(number)
- Rnd()
- The Rnd() function is used to Return a randomly generated value between 0 and 1.
- Syntax: Rnd(num)
- Val()
- Val() function is used to convert a numeric string into an integer number.
- Syntax: Val(numeric_string)
- Example: Val(“245”)
Output: 245 [in numeric form]
(2.) VB String in-Built Functions
- Asc()
- The function Asc() is used to obtain the corresponding ASCII value of the given character (letter).
- Syntax: Asc(character)
- Example:
Sub Main()
Dim val As Integer
val = Asc(“m”)
Console.WriteLine(“Ascii value = {0}”, val)
End Sub
End Module
- Chr()
- The Chr() function returns the corresponding ASCII value for the character(numeric value).
- Syntax: Chr(Num)
- Example:
- CStr()
- This function is used to convert the value of different data types into a string type.
- Syntax: CStr(val)
- InputBox()
-
The InputBox() function displays a pop-up input box to take user inputs at run time with a user-customized message.
-
Syntax : returnString = InputBox (prompt, title, defaultText, xpos, ypos)
-
The returnString is the value returned by the InputBox() function which is the text entered by the user.
-
The prompt parameter is a text string (either a string literal or a string variable) given by the programmer that prompts the user to guide/enter some information.
-
The title parameter is another string literal or string variable that supplies the title for the input box.
-
The defaultText parameter can be used to enter default content in the input box (although it would probably leave blank in most cases).
-
The xpos and ypos parameters specify the x and y coordinates for the input box on the screen.
-
-
- LCase()
- The LCase() function is used to convert the specified string into a lowercase string.
- Syntax: LCase(String)
- LTrim()
- This function removes the extra white space (if any) at the left-hand end of the text string.
- Syntax: LTrim(Str)
- Msgbox()
-
The MsgBox() function displays a customized message in a pop-up message box.
-
The format/syntax of the statement used to invoke a message box is as follows: –returnVal = MsgBox (prompt, styleVal, title)
- The prompt parameter is a string value (either a string literal or a string variable) that gives the message to be displayed.
- The styleVal parameter is either an integer style value, from 0 to 5, or a named constant that can be used instead of the corresponding integer value, that determines which command buttons will appear on the message box.
- The title parameter is another string literal or string variable that supplies the title for the message box.
-
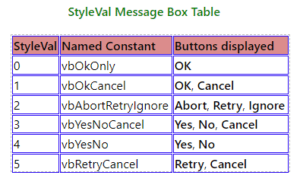
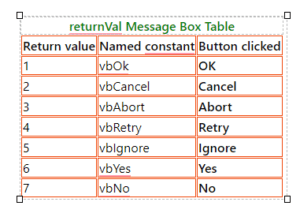
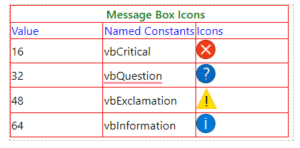
-
- For Example:
(i) MsgBox (“This message is for info!”, 64, “Info”)
(ii) MsgBox (“This message is for info!”, vbOKOnly + vbInformation, “Info”)
- RTrim()
- This function removes the extra white space (if any) at the right-hand end of the text string.
- Syntax: RTrim(Str)
- Trim()
- This function removes the extra white space (if any) at either end of the text string.
- Syntax: Trim(Str)
- UCase()
- The UCase() function is used to convert the specified string into an uppercase string.
- Syntax: UCase(String)
(3.) VB Date & Time in-Built Functions
- Format() [ For more details use this link ]
- The Format() function is used to specify how date and time values are displayed.
- Syntax: Format (Date/Now, “stylearguments”)
Here, styleArguments value may be –
| Style Arguments | Description |
| “General Date” | Displays the date and time value in the format – dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:ss |
| “Long Date” | Displays the date value in the format – 06 October 2009 |
| “Short Date” | Displays the date value in the format – dd/mm/yyyy |
| “Long Time” | Displays the time value in the format – h:mm:ss |
| “Short Time” | Displays the time value in the format – hh:mm |
- Now() – This function returns the current date and time.
- DateDiff(DateInterval.Day, date1, date2) – It gives the difference between two dates.
(B) User-defined Functions
- These are user-defined, customized functions created to perform specific tasks.
- It may be –
-
ByVal (Call by Value)
- In VB.NET, ByVal is a keyword used to specify how arguments are passed to methods (procedures or functions).
- In this, a copy of the variable is passed as a parameter to the method.
- Here, any changes made to the parameter inside the method do not affect the original variable outside the method.
- This concept is used especially when we want to ensure the original variable remains unchanged.
- Syntax :
-
ByRef (Call by Reference)
- In VB.NET, ByRef is a keyword used to specify how an argument is passed to methods (procedures or functions).
- In this, a reference of the actual variable is passed as a parameter to a method.
- Here, any changes made to the parameter inside the method will affect the original variable outside the method.
- This concept is used when we need the method to modify the original variable’s value.
- Syntax :
(C) Recursive Functions
- Recursive Functions are special functions that call themselves in their processing are called recursive functions.
- These are useful for repetitive tasks like calculating factorials or traversing trees etc.
- For example –
(D) Overloaded Functions
- Functions with the same name but different parameter lists (signature). Overloading allows for flexibility with varying types of input.
- This function is similar to function overloading, discussed in the class object program example.
- These are the Functions that belong to the class rather than an instance of the class.
- They are accessed using the class name.
- For example –
![]()
0 Comments