Table of Contents
hide
- A typical and basic program structure of VB.Net normally consists of the following components:-
- Namespace (One or more)
- Comments(one or more – anywhere in the program)
- A Class or Module
- Procedures(One or more – includes Subroutines, Functions, Operators, Handlers, Get, Set etc.) Codes contains
- The main procedure
- Variables declaration
- Statements & Expressions
- Procedures(One or more – includes Subroutines, Functions, Operators, Handlers, Get, Set etc.) Codes contains
- A Class or Module
Ways of VB .Net Programming
- VB .Net supports two basic ways of programming –
- in CUI mode(through command line/console application) and
- in GUI mode(through Form Application).
- To open & run the Console application in VB .Net 2013 : Open Visual Studio 2013 first – File menu – New – Project – Template – Visual Basic – Console Application – ok – Type the codes in the main procedure of module – press F5/Start from Standard toolbar to run the program – Output appears in Console.
To run the console program using the command line, open the command prompt tool and go to the directory where we saved the file – Type ‘vbc savedfilename(say program1.vb) and press enter to compile the code – if no errors, type program1.exe/program1 to run the program – Output appears on the console.
- Example of Console Application :
Example : (Using Module)
'A simple basic program structure in vb .net through console way using Module.
Imports System
Module Module1
Sub Main()
Console.WriteLine("Hello Users")
Console.ReadKey()
End Sub
End Module
NB : Save as - program1.vb
Example :(Using subroutine in Class Object)
Imports System
Public Class Rectangle
Dim length As Integer
Dim width As Integer
Dim result As Integer
'Private length As Integer
'Private width As Integer
'Private result As Integer
Public Sub Input()
length = 20
width = 30
End Sub
Public Sub Process()
result = length * width
End Sub
Public Sub Display()
Console.WriteLine("Length: {0}", length)
Console.WriteLine("Width: {0}", width)
Console.WriteLine("Area: {0}", result)
End Sub
Shared Sub Main()
Dim Obj1 As New Rectangle()
Obj1.Input()
Obj1.Process()
Obj1.Display()
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Class
Example :(Using Function in Class Object)
Imports System
Public Class Rectangle
Dim length As Integer
Dim width As Integer
Dim result As Integer
'Dim length=20, width=30, result As Integer
'Dim length As Integer=20
'Dim width As Integer=30
'Dim result As Integer
Function Input() As Integer
length = 20
width = 30
Return 0
End Function
Function Process() As Integer
result = length * width
Return 0
End Function
Function Display() As Integer
Console.WriteLine("Length is : {0}", length)
Console.WriteLine("Width is : {0}", width)
Console.WriteLine("Area of rectangle is: {0}", result)
Return 0
End Function
Shared Sub Main()
Dim Obj1 As New Rectangle()
Obj1.Input()
Obj1.Process()
Obj1.Display()
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Class
Example of Form Applications
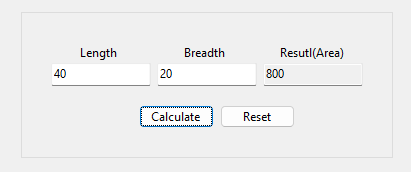
(Example : Area of Rectangle)
Public Class FrmAreaofRectangle
Private Sub BtnCalculate_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnCalculate.Click
TxtResult.Text = Val(TxtLength.Text) * Val(TxtBreadth.Text)
End Sub
Private Sub BtnReset_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles BtnReset.Click
TxtLength.Text = ""
TxtBreadth.Text = ""
TxtResult.Text = ""
TxtLength.Focus()
End Sub
Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
TxtLength.Focus()
TxtResult.ReadOnly = True
End Sub
End Class
0 Comments